
Juno Magnetic Field Investigation - Instruments
The magnetometer instruments will measure the magnetic properties of Jupiter. On Earth, a magnetic field surrounds the planet. The magnetism results from electric currents circulating in the molten iron churning slowly in the Earth's core. Jupiter has a stronger global magnetic field than Earth. Magnetic fields are usually measured in units of "gamma", for our purposes we use the equivalent "nanoTesla" unit.The Advanced Stellar Compass (ASC) will provide accurate information about the Juno spacecraft pointing for precise mapping.
Unlike the other instruments, the magnetometer sensors and ASC will not be attached to the main body of the spacecraft. Instead, the sensors will sit at the end of one of the three solar panels. This placement ensures that the data generated from the magnetometer sensors will not be "polluted" by magnetic signals from the spacecraft system.
Fluxgate Magnetometer
The fluxgate magnetometers (FGM) for the Juno mission are based on similar instruments developed for numerous previous missions Voyager, Magsat, International Solar Polar mission, Giotto, Active Magnetospheric Particle Tracer Explorers, Mars Global Surveyor, etc.). The basic configuration consists of dual; wide-range, triaxial flux gate sensors mounted remote from the spacecraft's body. Assuming that this field is primarily dipolar in nature at the location of the magnetometer sensors, the ambient field can then be analytically determined by combining the outboard and inboard measurements.In a magnetometer of this type, the nonlinearity of magnetization properties for the high permeability of easily saturated ferromagnetic alloys provides an indicator of the local field strength. The word "fluxgate" is used to refer to the method of periodic switching of magnetic flux in the detector.
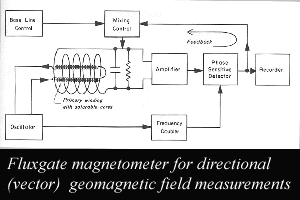
Click on picture for larger view
The FGM is being built by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in Greenbelt, Maryland, U.S.A.
Advanced Stellar Compass
The Advanced Stellar Compass (ASC) will be used to provide accurate information about the Juno spacecraft pointing. The ASC will consist of CCD cameras and a Data Processing Unit. It will be able to determine direction with arc sesond accuracy. The ASC is being built by the Technical University of Denmark (DTU).- Privacy Policy and Important Notices.
- Last Modified: 22 January 2025
- NASA Official: Ron Oliversen
- Email: Ronald.J.Oliversen@nasa.gov
- Curator: Ever Guandique, ADNET Systems, Inc.
- Email: ever.guandique@nasa.gov